
Brought to you by:
Enterprise Strategy Group | Getting to the Bigger Truth™
ESG TECHNICAL REVIEW
Manage and Protect Kubernetes with Kasten by Veeam
By Craig Ledo, IT Validation Analyst; and Vinny Choinski, Senior Analyst
MARCH 2022
Abstract
The Challenges
Figure 1. Top Five Backup/Disaster Recovery Challenges for Container Environments
What are your biggest challenges related to managing backup/disaster recovery for container environments? (Percent of respondents, N=334, three responses accepted)
Source: Enterprise Strategy Group
The Solution: Kasten K10 Platform for Kubernetes
Figure 2. Kasten for Kubernetes Overview

Source: Enterprise Strategy Group
ESG Validated
Distributed Cloud Data Management
Figure 3. Cluster Status Overview
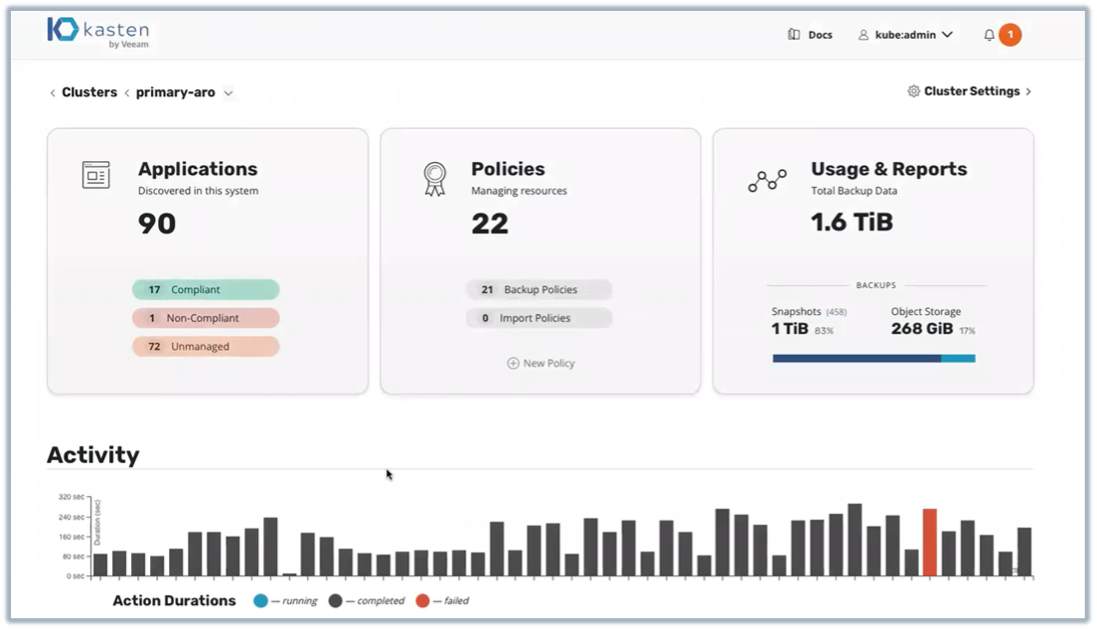
Source: Enterprise Strategy Group
Backup Policy
Figure 4. Backup Policy Management
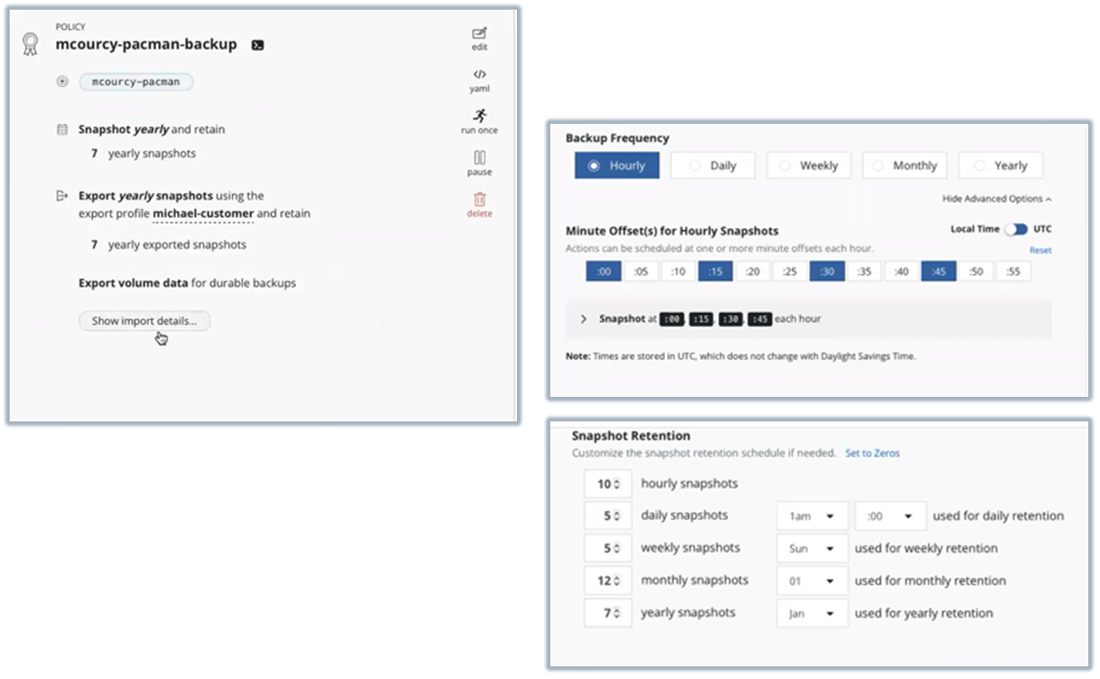
Source: Enterprise Strategy Group
Figure 5. Distributed Cloud Backup and Recovery
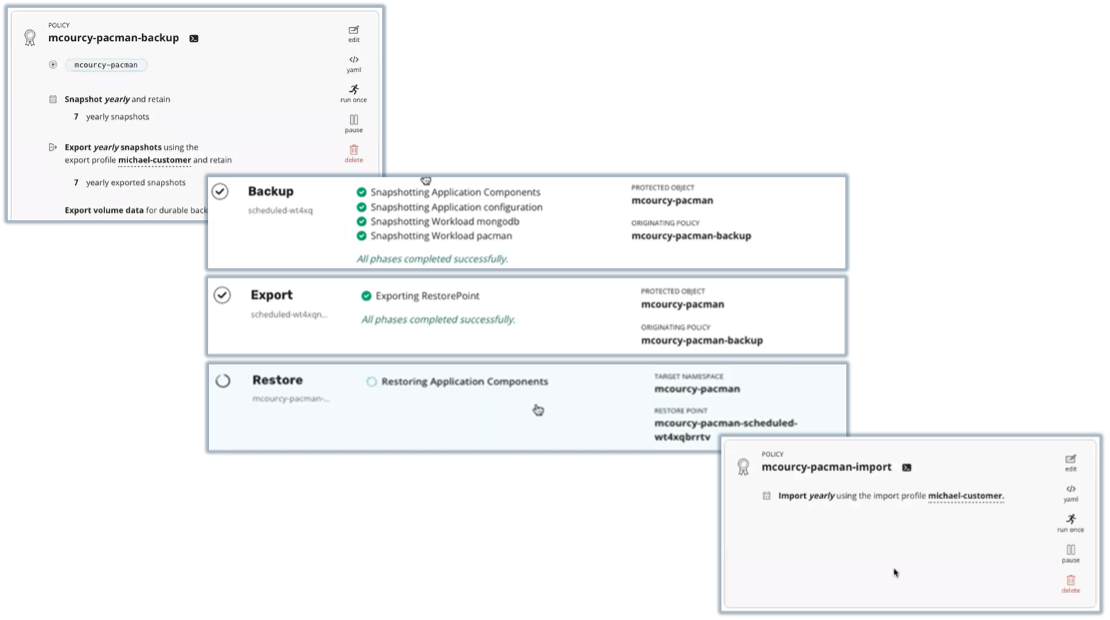
Source: Enterprise Strategy Group
Why This Matters
Usage & Reports – Cluster Reports
Figure 7. Usage & Reports – Cluster Reports
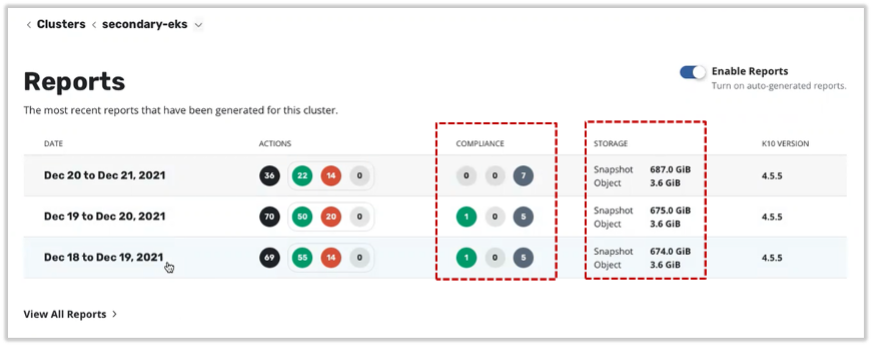
Source: Enterprise Strategy Group
Usage & Reports - Data Usage
Figure 8. Usage & Reports – Data Usage
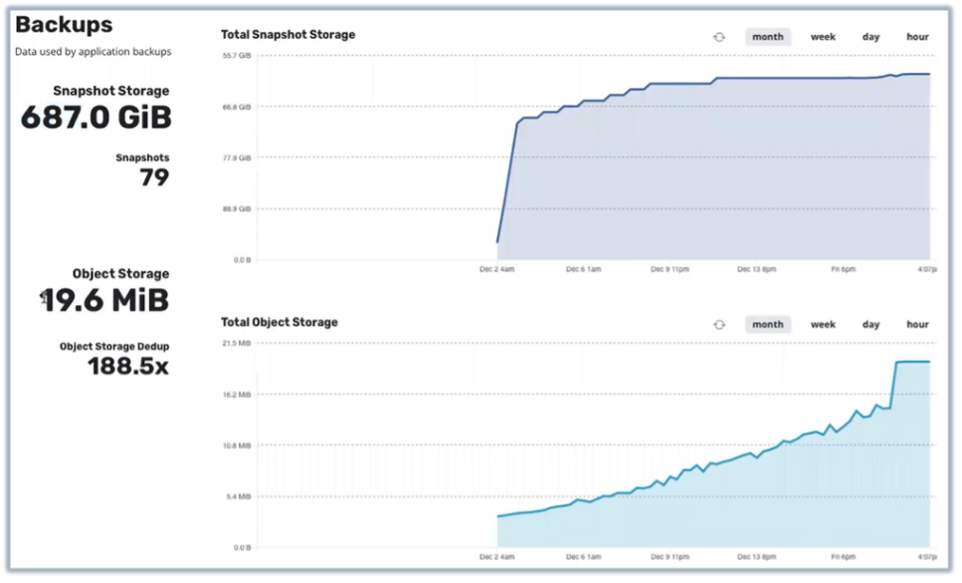
Source: Enterprise Strategy Group
Why This Matters
The Bigger Truth
This ESG Technical Review was commissioned by Veeam and is distributed under license from ESG.
All trademark names are property of their respective companies. Information contained in this publication has been obtained by sources The Enterprise Strategy Group (ESG) considers to be reliable but is not warranted by ESG. This publication may contain opinions of ESG, which are subject to change from time to time. This publication is copyrighted by The Enterprise Strategy Group, Inc. Any reproduction or redistribution of this publication, in whole or in part, whether in hard-copy format, electronically, or otherwise to persons not authorized to receive it, without the express consent of The Enterprise Strategy Group, Inc., is in violation of U.S. copyright law and will be subject to an action for civil damages and, if applicable, criminal prosecution. Should you have any questions, please contact ESG Client Relations at 508.482.0188.

Enterprise Strategy Group | Getting to the Bigger Truth™
Enterprise Strategy Group is an IT analyst, research, validation, and strategy firm that provides market intelligence and actionable insight to the global IT community.
